Secured NiFi cluster with NiFiKop on the Google Cloud Platform
Credits
Before starting, I wanted to mention the fact that this post is an adaptation of the Pierre Villard's one: Secured NiFi cluster with Terraform on the Google Cloud Platform
Objectives
In this article, we'll use NiFiKop and Terraform to quickly:
- deploy a GKE cluster to host our NiFi cluster,
- deploy a
cert-managerissuer as a convenient way to generate TLS certificates, - deploy a zookeeper instance to manage cluster coordination and state across the cluster,
- deploy X secured NiFi instances in cluster mode
- configure NiFi to use OpenId connect for authentication
- configure HTTPS loadbalancer with Client Ip affinity to access to the NiFi cluster
- re-size the cluster dynamically
Pre-requisites
- You have your own domain (you can create on with Google): it will be used to map a domain to the NiFi's web interface. In this post, we will use:
trycatchlearn.fr.
Disclaimer
This article can get you started for a production deployment, but should not used as so. There is still some steps needed such as Zookeeper configuration etc.
Create OAuth Credentials
First step is to create the OAuth Credential:
- Go to your GCP project, and in the left bar: APIs & Services > Credentials
- Click on
CREATE CREDENTIALS: OAuth client ID - Select
Web Application - Give a name like
SecuredNifi. - For
Authorised JavaScript origins, use your own domain. I'm using:https://nifisecured.trycatchlearn.fr:8443 - For
Authorised redirect URIsit's your previous URI +/nifi-api/access/oidc/callback, for me:https://nifisecured.trycatchlearn.fr:8443/nifi-api/access/oidc/callback
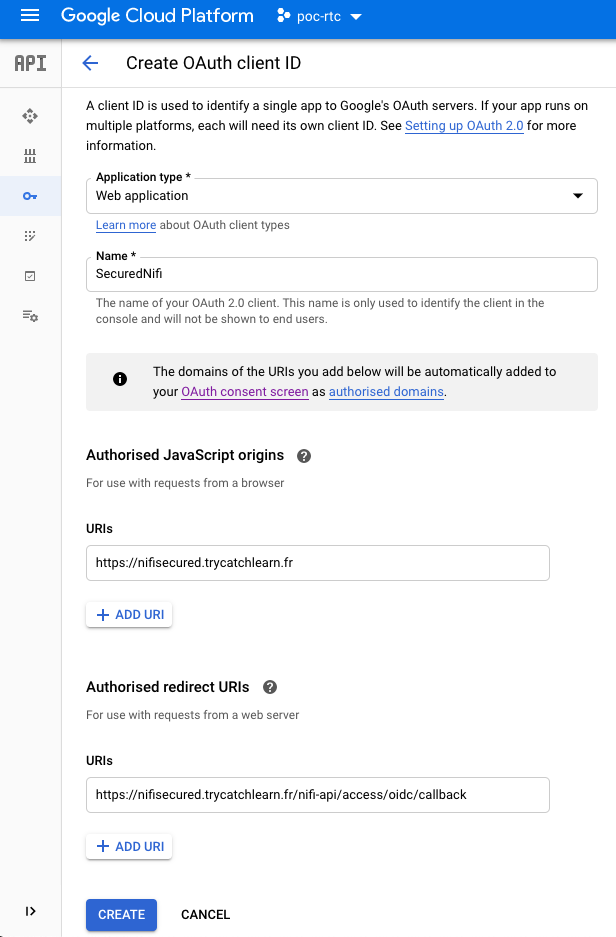
- Create the OAuth credentials
Once the credentials are created, you will get a client ID and a client secret that you will need in NifiCluster definition.
Create service account
For the GKE cluster deployment you need a service account with Editor role, and Kubernetes Engine Admin.
Deploy secured cluster
Once you have completed the above prerequisites, deploying you NiFi cluster will only take three steps and few minutes.
Open your Google Cloud Console in your GCP project and run:
git clone https://github.com/konpyutaika/nifikop/nifikop.git
cd nifikop/docs/tutorials/secured_nifi_cluster_on_gcp
Deploy GKE cluster with Terraform
Deployment
You can configure variable before running the deployment in the file terraform/env/demo.tfvars:
- project: GCP project ID
- region: GCP region
- zone: GCP zone
- cluster_machines_types: defines the machine type for GKE cluster nodes
- min_node: minimum number of nodes in the NodePool. Must be >=0 and <= max_node_count.
- max_node: maximum number of nodes in the NodePool. Must be >= min_node_count.
- initial_node_count: the number of nodes to create in this cluster's default node pool.
- preemptible: true/false using preemptibles nodes.
- nifikop_image_repo: NiFiKop's image repository
- nifikop_image_tag: NiFiKop's image tag
- nifikop_chart_version: NiFiKop's helm chart version
./start.sh <service account key's path>
This operation could take 15 minutes (time to the GKE cluster and its nodes to setup)
Once the deployment is ready load the GKE configuration:
gcloud container clusters get-credentials nifi-cluster --zone <configured gcp zone> --project <GCP project's id>
Explanations
The first step is to deploy a GKE cluster, with the required configuration, you can for example check the nodes configuration:
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
gke-nifi-cluster-tracking-ptf20200520-a1aec8fe-2dl3 Ready <none> 110m v1.15.9-gke.24
gke-nifi-cluster-tracking-ptf20200520-a1aec8fe-5bzb Ready <none> 110m v1.15.9-gke.24
gke-nifi-cluster-tracking-ptf20200520-a1aec8fe-5t3l Ready <none> 110m v1.15.9-gke.24
gke-nifi-cluster-tracking-ptf20200520-a1aec8fe-w86j Ready <none> 110m v1.15.9-gke.24
Once the cluster is deployed, we created all the required namespaces:
kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
cert-manager Active 106m
default Active 116m
kube-node-lease Active 116m
kube-public Active 116m
kube-system Active 116m
nifi Active 106m
zookeeper Active 106m
In the cert-manager namespace we deployed a cert-manager stack in a cluster-wide scope, which will be responsible for all the certificates generation.
in this post, we will let cert-manager create a self-signed CA.
For more information check documentation page
kubectl -n cert-manager get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cert-manager-55fff7f85f-74nf5 1/1 Running 0 72m
cert-manager-cainjector-54c4796c5d-mfbbx 1/1 Running 0 72m
cert-manager-webhook-77ccf5c8b4-m6ws4 1/1 Running 2 72m
It will also deploy the Zookeeper cluster based on the bitnami helm chart:
kubectl -n zookeeper get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
zookeeper-0 1/1 Running 0 74m
zookeeper-1 1/1 Running 0 74m
zookeeper-2 1/1 Running 0 74m
And finally it deploy the NiFiKop operator which is ready to create NiFi clusters:
kubectl -n nifi get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nifikop-849fc8548f-ss6w4 1/1 Running 0 74m
Deploy Secured NiFi cluster
You will now deploy your secured cluster to do so edit the kubernetes/nifi/secured_nifi_cluster.yaml and set with your own values:
apiVersion: nifi.orange.com/v1alpha1
kind: NifiCluster
metadata:
name: securednificluster
namespace: nifi
spec:
...
initialAdminUser: <your google account email>
readOnlyConfig:
# NifiProperties configuration that will be applied to the node.
nifiProperties:
webProxyHosts:
- <nifi's hostname>:8443
# Additionnal nifi.properties configuration that will override the one produced based
# on template and configurations.
overrideConfigs: |
...
nifi.security.user.oidc.client.id=<oidc client's id>
nifi.security.user.oidc.client.secret=<oidc client's secret>
...
- Spec.InitialAdminUser: Your GCP account email (this will give you the admin role into the NiFi cluster), in my case
aguitton.ext@orange.com - Spec.ReadOnlyConfig.NifiProperties.WebProxyHosts[0]: The web hostname configured in the Oauth section, in my case
nifisecured.trycatchlearn.fr - Spec.ReadOnlyConfig.NifiProperties.OverrideConfigs: you have to set the following properties:
- nifi.security.user.oidc.client.id: OAuth Client ID
- nifi.security.user.oidc.client.secret: OAuth Client secret
Once the configuration is ok, you can deploy the NifiCluster:
kubectl create -f kubernetes/nifi/secured_nifi_cluster.yaml
After 5 minutes your cluster should be running:
kubectl get pods -n nifi
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nifikop-849fc8548f-ss6w4 1/1 Running 0 28h
securednificluster-0-node9tqff 1/1 Running 0 5m52s
securednificluster-1-nodew9tsd 1/1 Running 0 6m30s
securednificluster-2-nodemlxs8 1/1 Running 0 6m28s
securednificluster-3-nodeckw8p 1/1 Running 0 6m26s
securednificluster-4-nodewzjt7 1/1 Running 0 6m24s
Access to your secured NiFi Cluster
To finish you have to get the public IP of the load balancer:
kubectl -n nifi get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
securednificluster LoadBalancer 10.15.248.159 34.78.140.135 8443:30248/TCP,6007:30517/TCP,10000:31985/TCP 27m
securednificluster-headless ClusterIP None <none> 8443/TCP,6007/TCP,10000/TCP 27m
In my case it's 34.78.140.135.
We can now update the DNS records of your domains to add a DNS record of type A redirecting your hostname (in my case nifisecured.trycatchlearn.fr) to the load balancer IP.
I can now access the NiFi cluster using https://nifisecured.trycatchlearn.fr:8443/nifi and authenticate on the cluster using the admin account email address I configured in the NifiCluster resource.
Here is my 5-nodes secured NiFi cluster up and running:
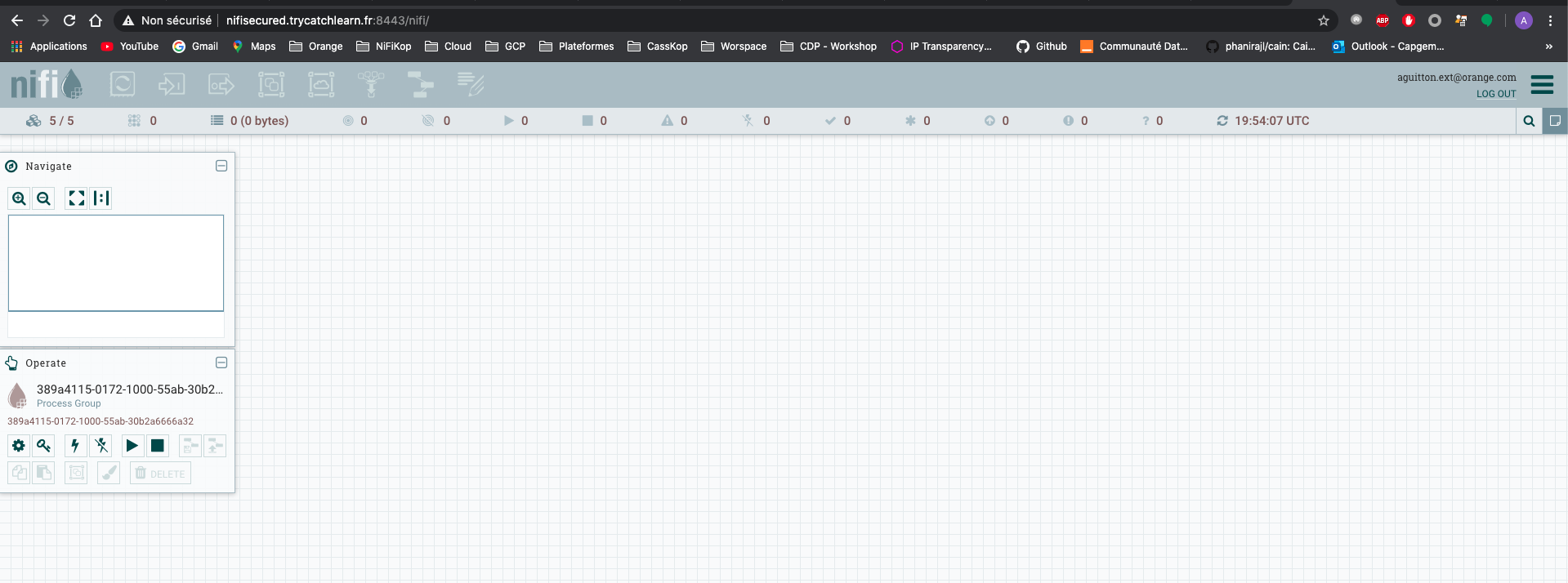
5-nodes secured NiFi cluster:
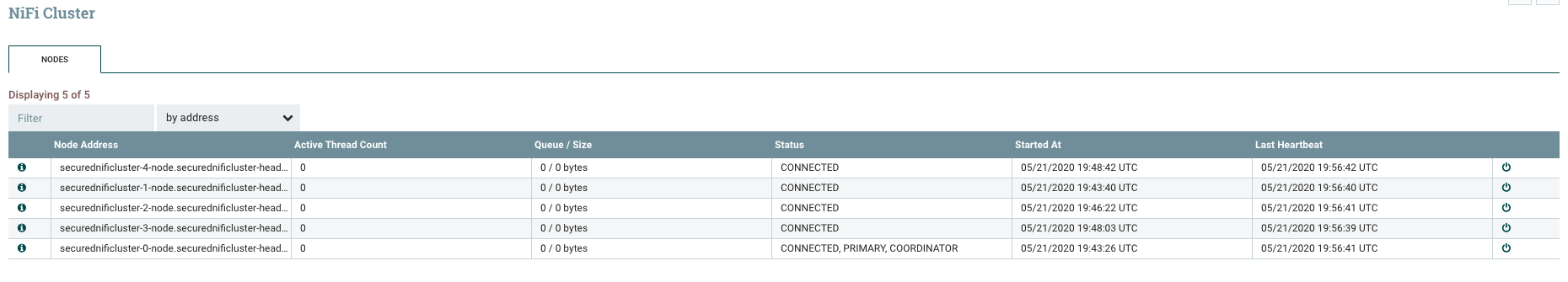
You can now update the authorizations and add additionnal users/groups.
Just have a look on documentation's page to finish cleaning setup.
Cleaning
To destroy all resources you created, you just need to run:
kubectl delete nificlusters.nifi.orange.com securednificluster -n nifi
kubectl delete crds nificlusters.nifi.orange.com
kubectl delete crds nifiusers.nifi.orange.com
./destroy.sh <service account key's path>